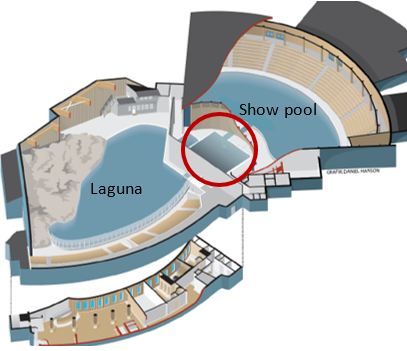
I conducted my research at Kolmården Zoo, Sweden. At the time of my study there were 12 Bottlenose Dolphins (Tursiops truncatus). The lay-out of the pool can be seen in the image next to the text. The enrichment sessions were held in the connecting holding pool (red circle) between the Laguna and the Show Pool. Cameras were used to record behaviour and a sound recorder to record echolocation.
Two enrichments were introduced to the dolphins: The Meandering Hose and The Shell Sand Boxes.
Click here to go to the Shell Sand Boxes section of the Material and Methods.
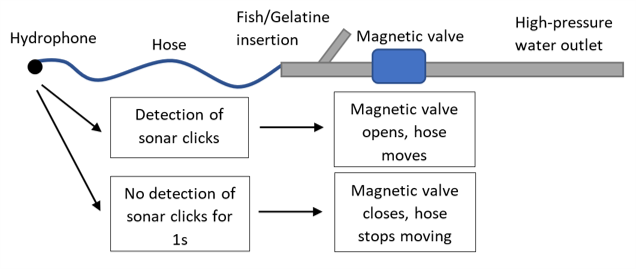
Meandering Hose
The meandering hose is a long plastic hose with a hydrophone at the end. The hydrophone is connected to an acoustic switch which will open for high pressure water flow when the hydrophone is hit by sonar clicks (see picture on the right). If no sonar is detected, the hose will not move. The meandering way the hose moves through due to the high-pressure water outlet simulates the movement of prey.
The hose had 5 different states it could be in:
Off: The water outlet was manually closed leaving the hose unresponsive to sonar.
On: The water outlet was opened when sonar clicks hit the hydrophone.
On + Fish: The water outlet was opened when sonar clicks hit the hydrophone and fish were ejected at semi-random intervals.
On + Gelatine: The water outlet was opened when sonar clicks hit the hydrophone and gelatine strips were ejected at semi-ranodm intervals.
On + Fish/Gelatine: The water outlet was opened when sonar clicks hit the hydrophone and gelatine strips and fish were ejected at semi-random intervals.
Behavioral and Acoustic Parameters
Multiple behavioural paramters were analysed. In brackets the behaviour types are noted.
* Observing (Exploratory): Being within 2 body lengths of the enrichment with head facing towards the hose.
* Direct Contact (Exploratory): Directly touching the hose with body.
* Physical Contact (Social): Direct contact with another dolphin.
* Snapping (Social): Direct contact with a conspecific with open mouth.
* High-Speed Purstuit (Foraging): Fast swimming when observing the hose. Usually started by a powerful movement with the fluke to get up to speed.
* Bubble Burst (Bubbles): A ‘cloud-like clustering of bubbles’ formed from the blowhole by releasing a large amount of air.
* Small Bubbles (Bubbles): A long and thin stream (line) of small bubbles ejected from the blowhole.
Several acoustic parameters were selected to be analysex=d from the sound data.
* The total number of clicks in the sound data of each session.
* The ratio of 10 ms buzzes in the sound data of each session.
* The ratio of 2 ms buzzes in the sound data of each session.
* The number of click trains in the sound data of each session.
* The average number of clicks per click train.
* The number of click trains with more than 500 clicks.
* The number of click trains with more than 100 clicks.
* The ratio of how many of the click trains with more than 100 clicks were click trains with more than 500 clicks in the click train.
Shell Sand Boxes
Rossbach and Herzing (1997) observed wild dolphins in the Bahamas extracting fish from deep into the sea floor. This behaviour is called “crater feeding”. Their hypothesis was that dolphins might be able to detect these buried fish with their sonar.
A previous study was done with the sand boxes at Kolmården Zoo. Fish and gelatine were buried in the sand. Click detectors were placed below the sand box, in an attempt to monitor the dolphins’ search pattern, i.e., how they scanned the sand surface with their sonar beam. The results showed no indication that the dolphins detected the fish or gelatine lumps. This may be explained by the fact that the swim bladder of thawed fish is collapsed and hence the target strength of such a fish is very low. The gelatine lumps were supposed to create a hollow in the sand, which might be possible for the dolphins to distinguish from homogeneous sand, but this did not seem to be the case.
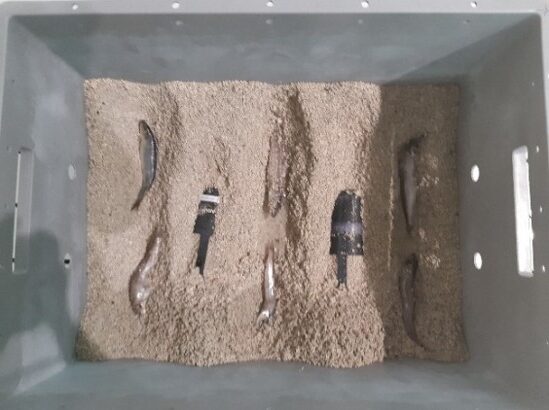
That is why, for my study the test setup is constructed of three boxes filled with shell sand, one of which also had two air-filled plastic tubes, with strong sonar target strength, as well as fish buried in the sand. The position of this box in restrospect to the other boxes was randomly changed between sessions

Behavioral Parameters
Multiple behavioural paramters were analysed. In brackets the behaviour types are noted.
* Observing In the Box (Exploratory): Body oriented in a vertical position above the box with head inside the box.
* Observing Above the Box (Exploratory): Body oriented in a vertical or horizontal position above the box, with head pointed towards the box but not being inside the box.
* Observing Outside the Box (Exploratory): Body oriented horizontally within a body length of the box. Head pointed towards the box.
* Snapping (Social): Direct contact with a conspecific with open mouth.
* Tail Slap (Foraging): A big, fast sweeping motion with the tail fluke, causing a powerful turbulence in the water.
* Bubble Burst (Bubbles): A ‘cloud-like clustering of bubbles’ formed from the blowhole by releasing a large amount of air.