Significant treatment results
Overall, there were 3 results where significant differences between treatments were found. In the judgment bias test, when examining the latency to start walking towards the stimuli in the 5-week-old chicks, there were significant differences between treatments (Figure 1, (F(1, 298) = 6.590; p = 0.011). The imprinted chicks were slower to start walking towards the morph than the control chicks (Figure 1, brown circle).
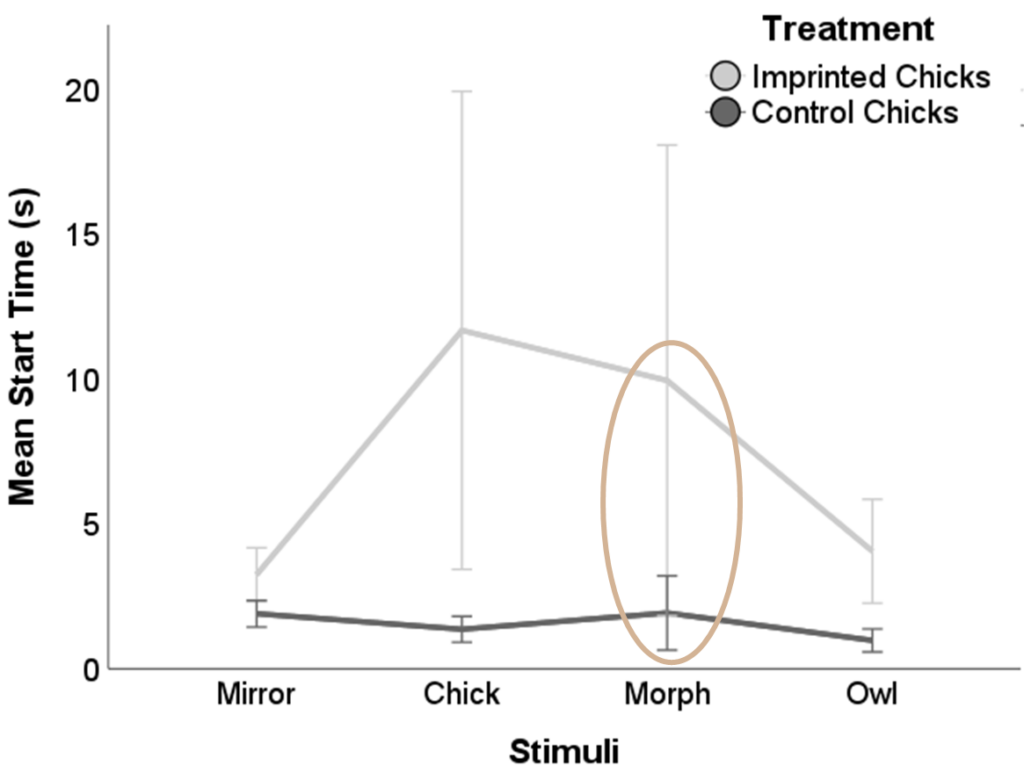
Figure 1. Latency to start walking towards the stimuli at 5 weeks of age, in imprinted chicks and control chicks. Error Bars: +/- 1 SE.
In the judgment bias test, when examining the latency to pass the stimuli in the 5-week-old chicks, there were significant differences between treatments (Figure 2, (F(1, 295) = 4.431; p = 0.036). However, there were no significant differences between treatments following Bonferroni correction (p > 0.025). The imprinted chicks were slower in passing the morph than the control chicks (Figure 2, brown circle).
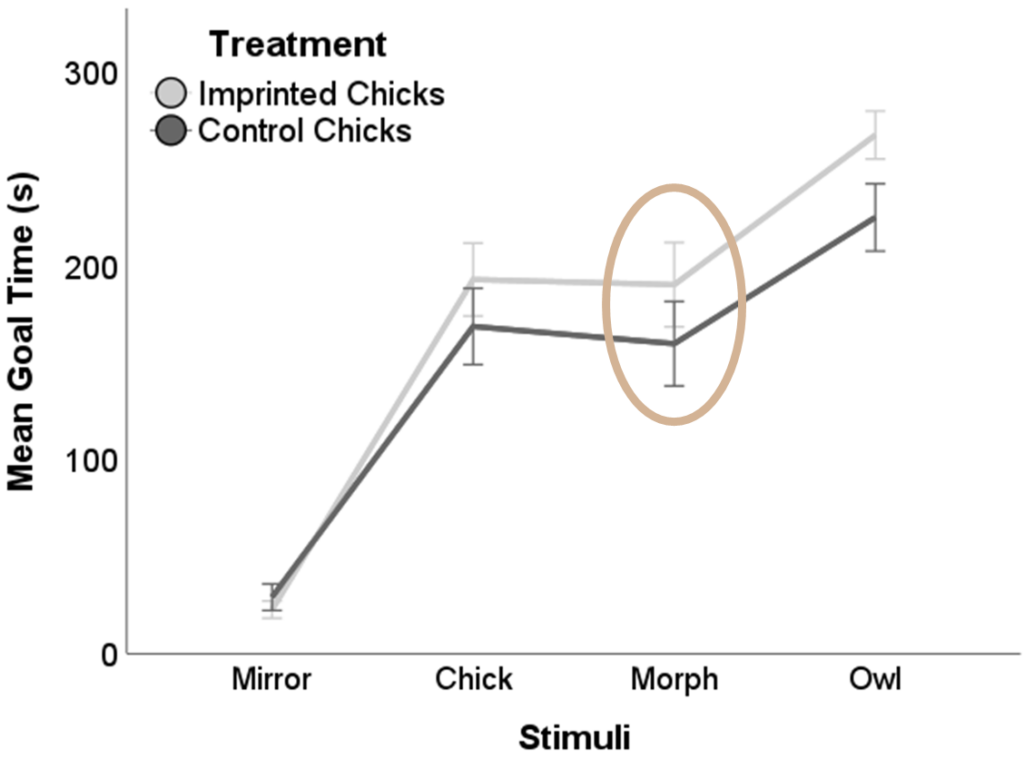
Figure 2. Latency to pass the stimuli at 5 weeks of age, in imprinted chicks and control chicks. Error Bars: +/- 1 SE.
When examining the body weight of the chicks, there were significant differences between treatments (Figure 3, (F(1, 523) = 18.336; p < 0.001). The imprinted chicks weighed less than the control chicks during all weigh-ins (Figure 3).
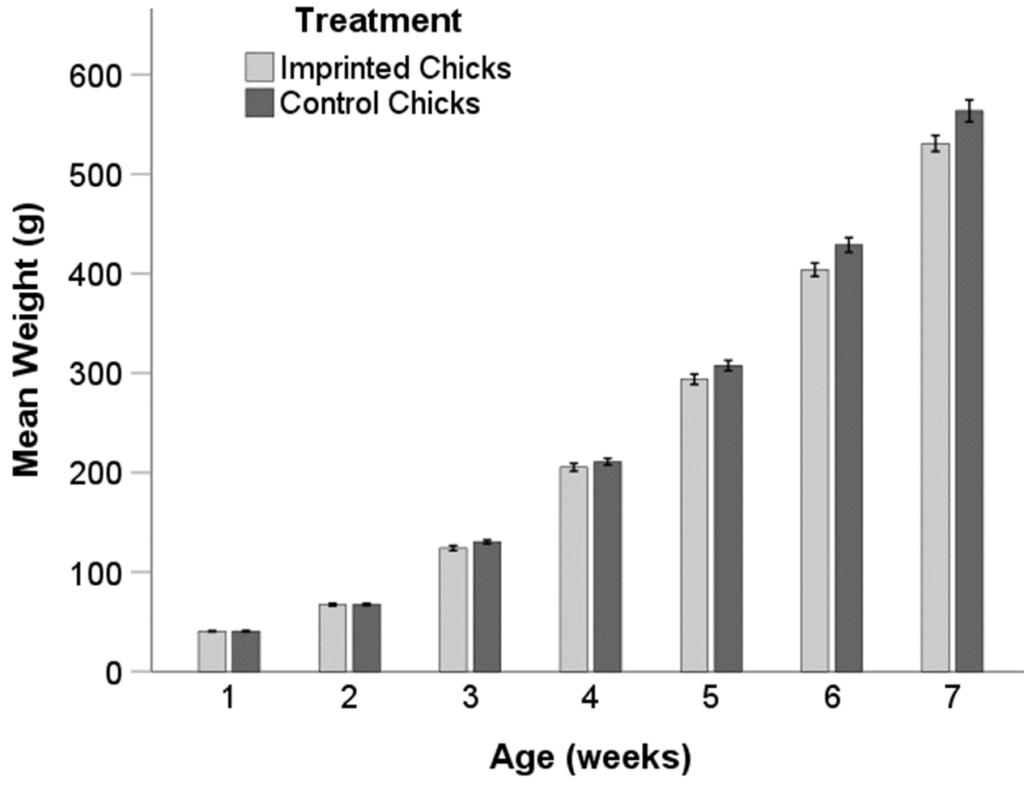
Figure 3. Body weight of imprinted chicks and control chicks at 1-7 weeks of age. Error Bars: +/- 1 SE.
Examples of non-significant treatment results
In the judgment bias test, when examining the latency to pass the stimuli in the 1-week-old chicks, there were no significant differences between treatments (Figure 4, (F(1, 270) = 1.855; p = 0.174).
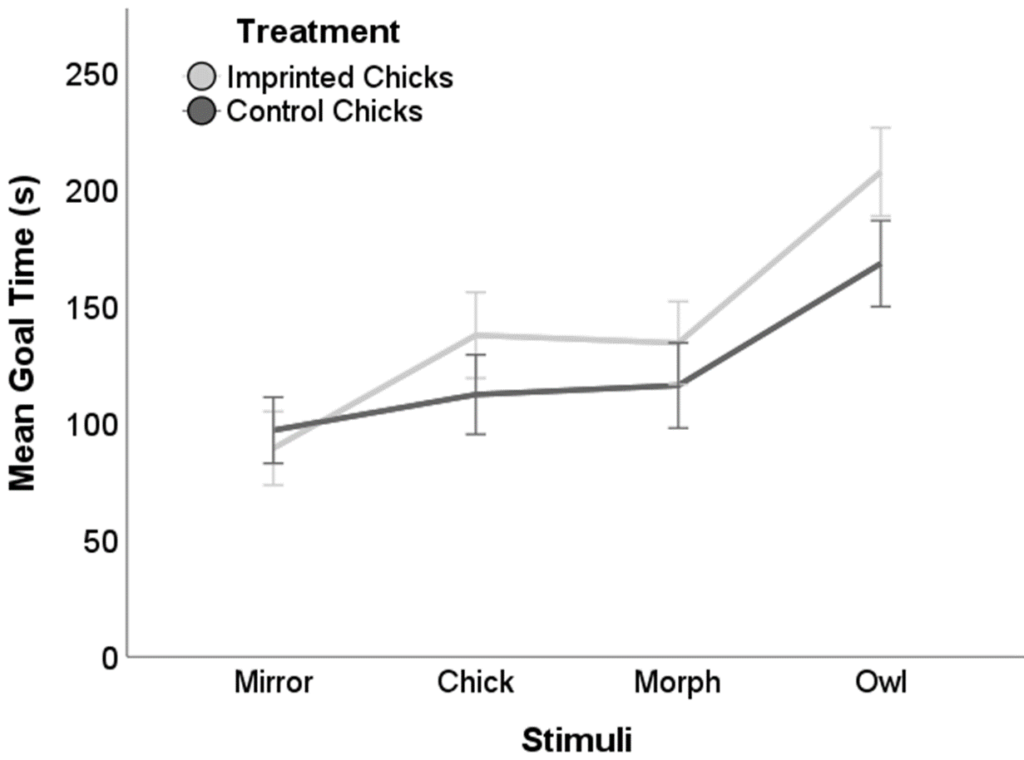
Figure 4. Latency to pass the stimuli at 1 week of age, in imprinted chicks and control chicks. Error Bars: +/- 1 SE.
In the open field test, when examining the number of escape attempts in the 1-week-old and 6-week-old chicks, there were no significant differences between treatments (Figure 5, (F(1, 150) = 0.390; p = 0.533).
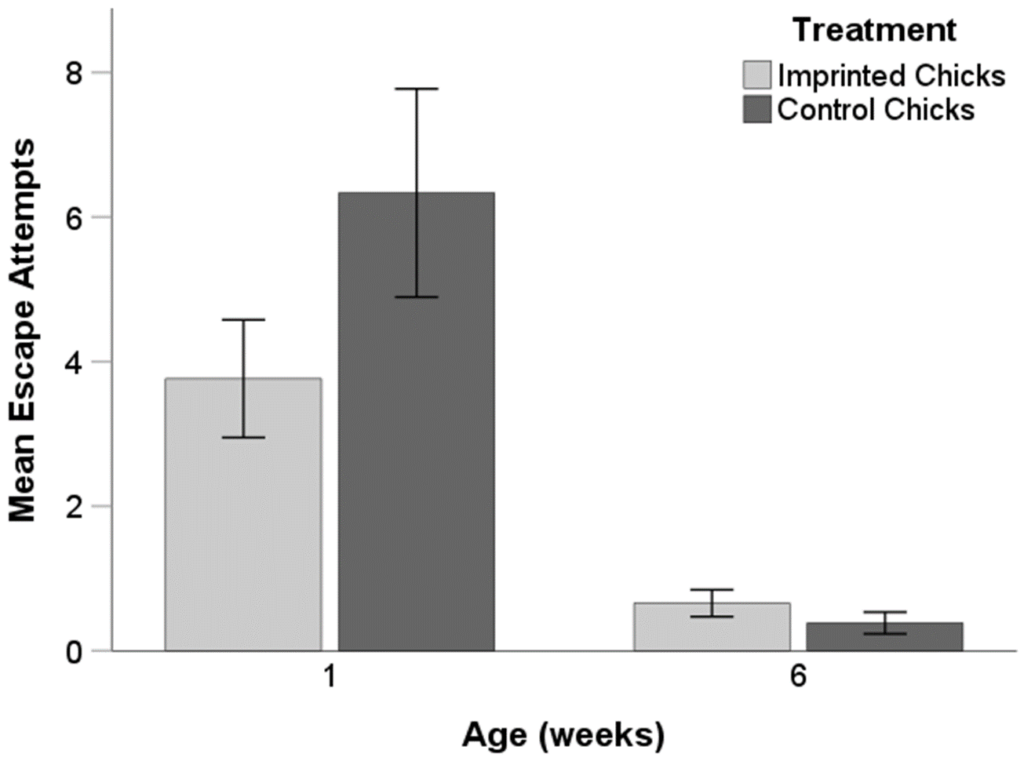
Figure 5. Number of escape attempts at 1 and 6 weeks of age, in imprinted chicks and control chicks. Error Bars: +/- 1 SE.
In the novel object test, when examining the number of line crossings in the 1-week-old and 6-week-old chicks, there were no significant differences between treatments (Figure 6, (F(1, 150) = 0.652; p = 0.421).
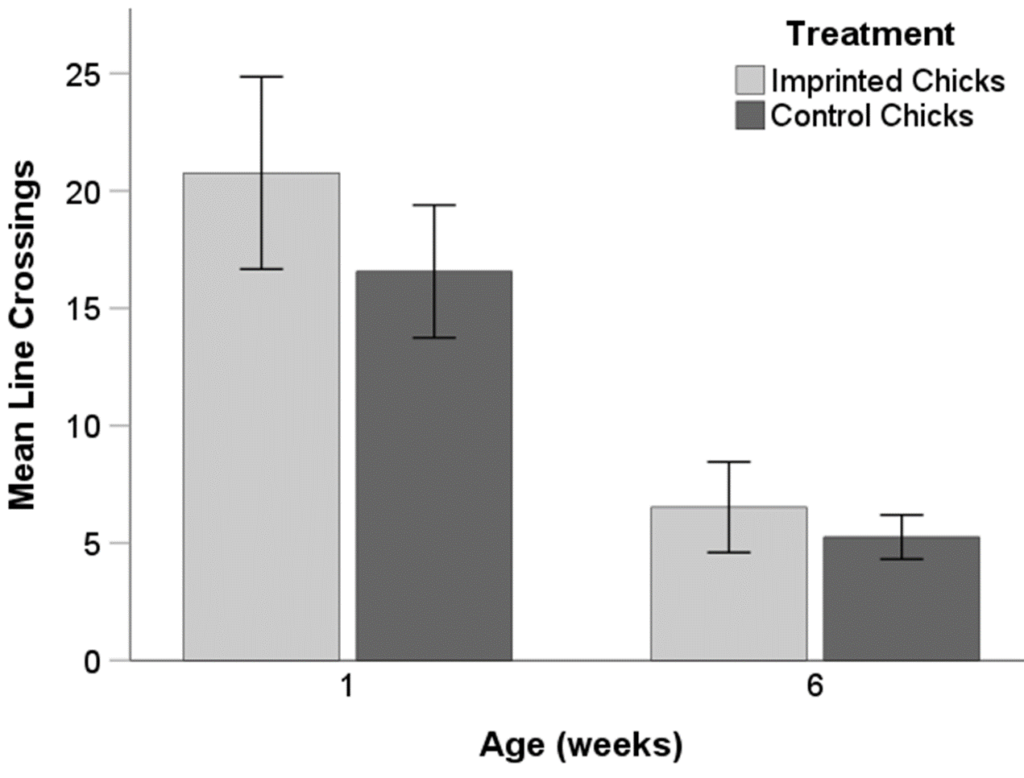
Figure 6. Number of line crossings at 1 and 6 weeks of age, in imprinted chicks and control chicks. Error Bars: +/- 1 SE.