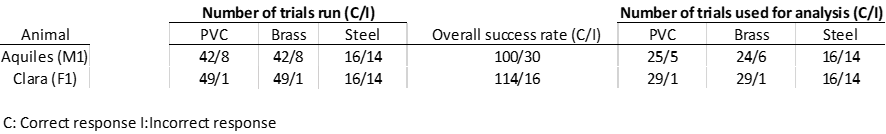
A total of 320 trials were performed with the two study dolphins (Table 1), with a minimum of 30 trials per material and animal.
Task performance and behaviour
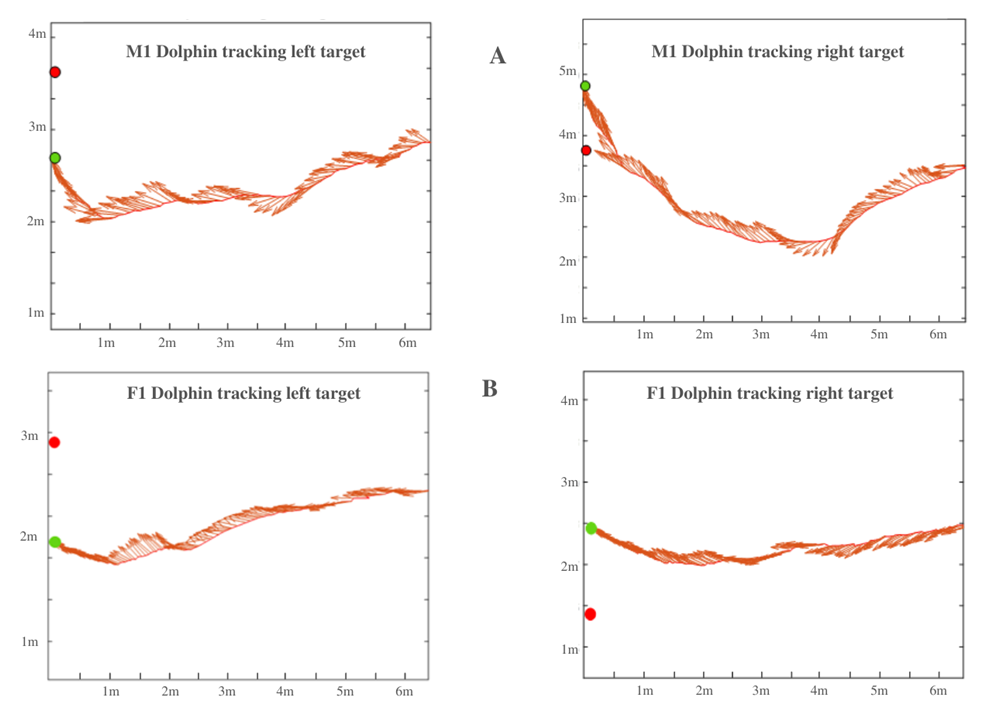
The male (M1) approached the targets with a curved swim path in all trials, keeping left away from the pool wall. The female (F1) used a frontal approach to the targets in 67.7% of the trials, and a slightly curved route in 33% of the trials.
Performance and target strength of the different materials
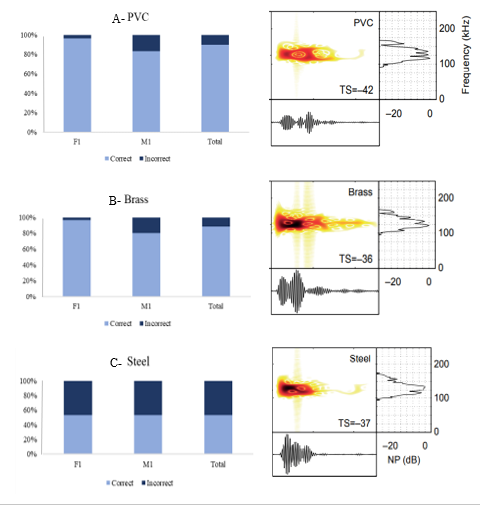
The dolphins made minor mistakes when discriminating the plastic or brass spheres from the aluminum sphere but the performance decreased when discriminating steel from aluminum sphere.
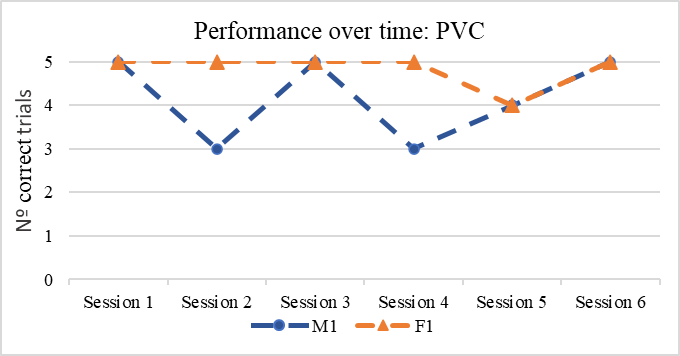
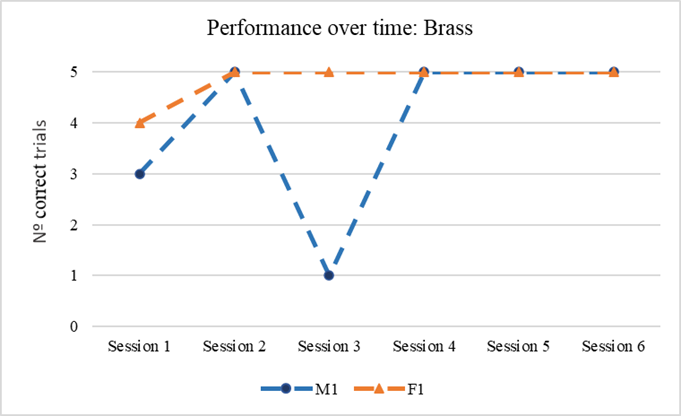
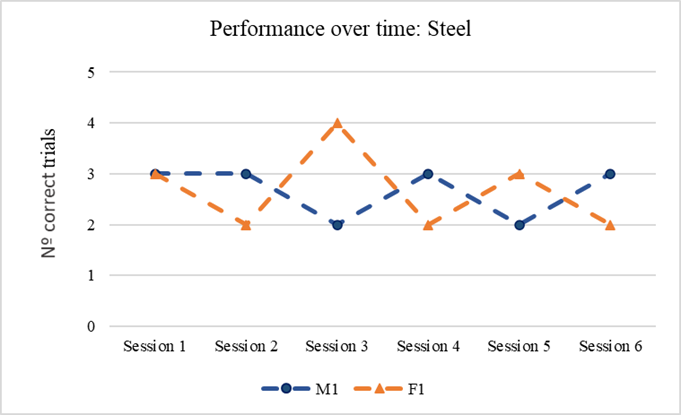
The performance of the two dolphins does not show any change over time, as would have been signs of learning.
Scanning behaviour
M1 scanned each target target before deciding on an average of 4.4 times for plastic, 3.3 times for brass and 4.8 times for steel. F1 scanned 3.6 times for plastic, 3.9 times for brass and 5.9 times for steel, increasing proportionally with the difficulty. In both dolphins the highest number of scans corresponds to the most difficult task.