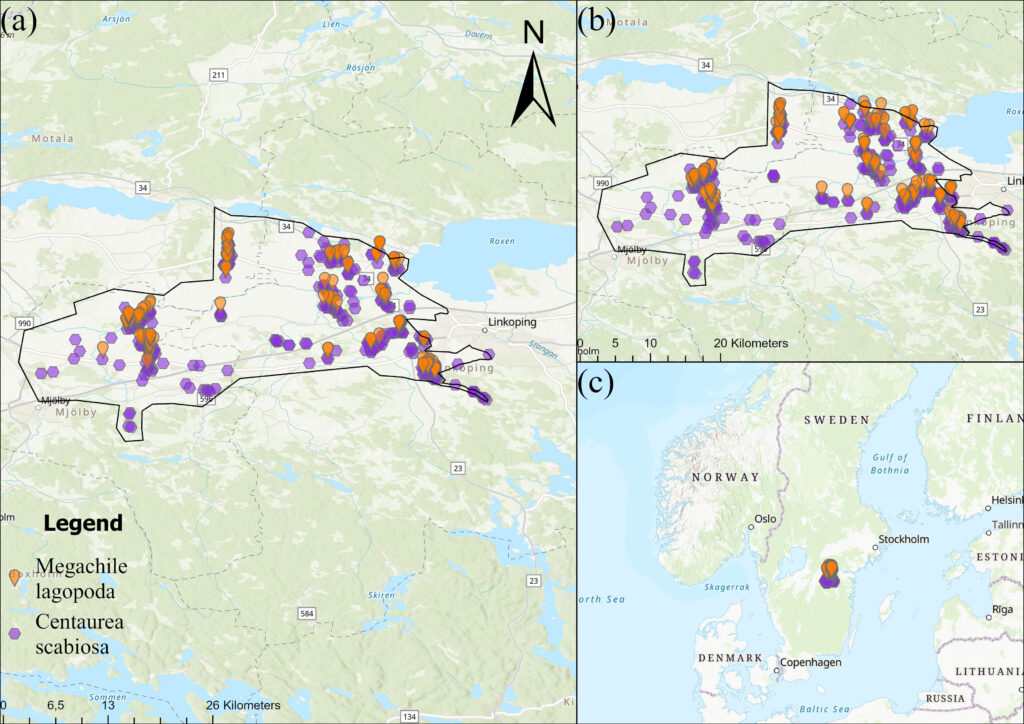
Study area
The fieldwork was conducted between June 1st and August 13th, 2024, covering approximately 400 km² between Linköping and Mjölby in Östergötland, Sweden. The study area was bounded by the Göta Canal to the north and the forest line to the south.
Study species
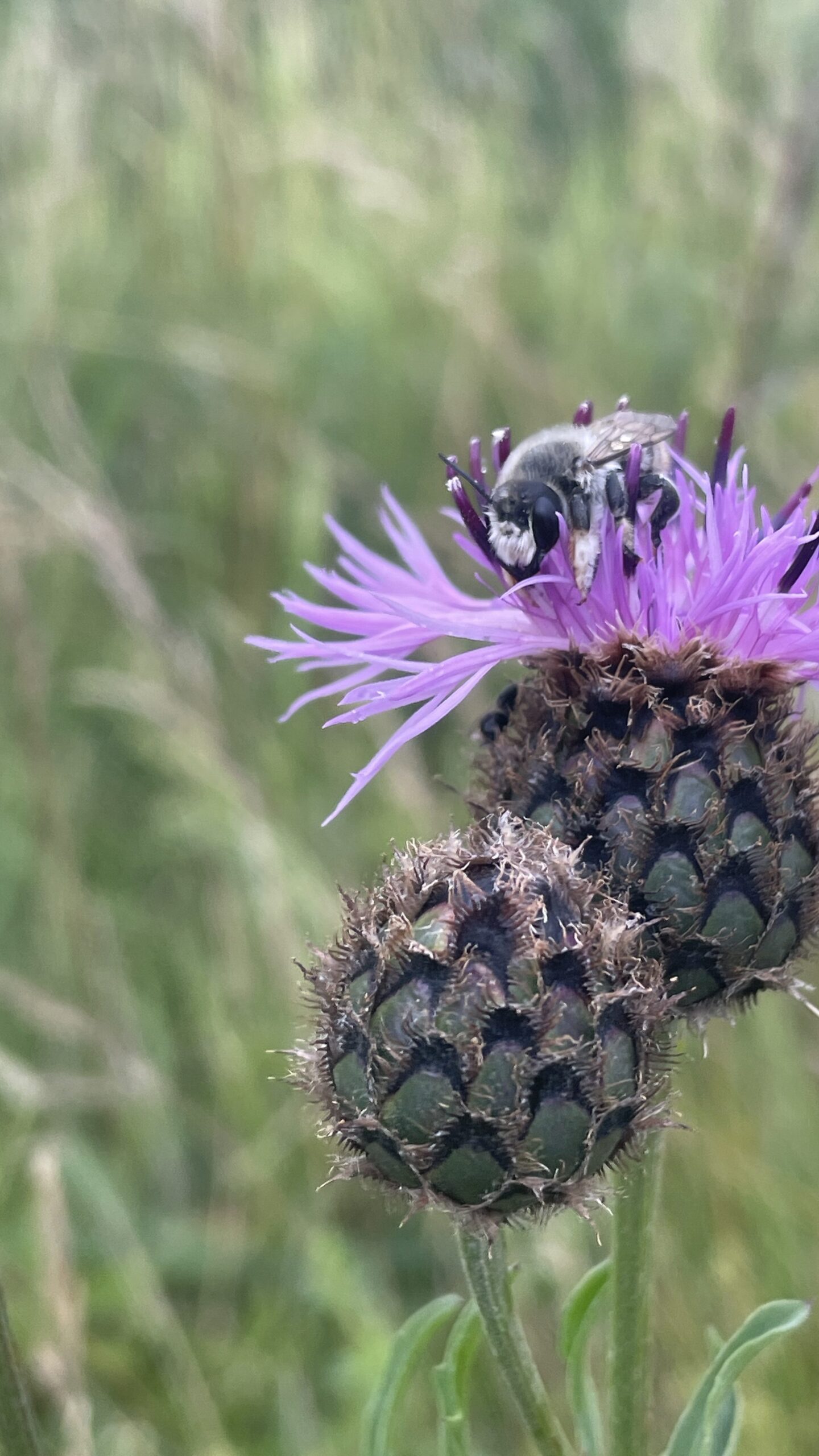
Megachile lagopoda is a specialist bee that collects pollen exclusively from Centaurea scabiosa. It inhabits sandy fields, dry meadows, and ruderal areas such as roadsides, quarries, and industrial sites. The species prefers south-facing slopes and sandhills for nesting and its main flight time spans from June to August.

Data collection
The data analysis consisted of the following components:
- Patch Identification: Initially, 275 small sites were mapped and then merged into 118 habitat patches if the edge-to-edge distance between them was ≤150m
- Survey Timing: Each site was visited at least three times during favorable weather conditions (>10°C, minimal to no precipitation) between 09:00-18:00
- Host Plant Quantification: Complete counts of Centaurea scabiosa stalks
- Bee Observations: Systematic walking transects through each patch to record all M. lagopoda sightings, noting GPS coordinates and sex
- Phenology Monitoring: Five sites with frequent bee visitation monitored every two days to document the end of the flight period
- Environmental Variables: Data on elevation range, ground moisture, soil type, shrub/tree height, and ground temperature extracted from existing spatial datasets
Statistical analysis
- Phenology: Calculated the proportion of total individuals observed on each sampling date, plotted separately for males and females
- Bee Presence/Absence: Generalized linear models (GLM) with binomial distribution using host plant abundance, connectivity measures, and environmental factors as predictors
- Bee Abundance: Generalized linear models with negative binomial distribution for occupied patches, examining factors influencing local population size
- Connectivity Analysis: Three measures calculated based on the incidence function model using a 150m dispersal distance parameter (population-weighted, occupied area, and patch presence)