Behaviours
In total 913 bats (repetition might occur) were observed. Among all the observed behaviours “hanging close” (712) was displayed the most often and “landing attempt” (4) the least. The same applies to the solitary category, while in the antagonistic category, “flapping wings” (142) was seen the most often and “chasing” (10) the least (Figure 1).

Activity
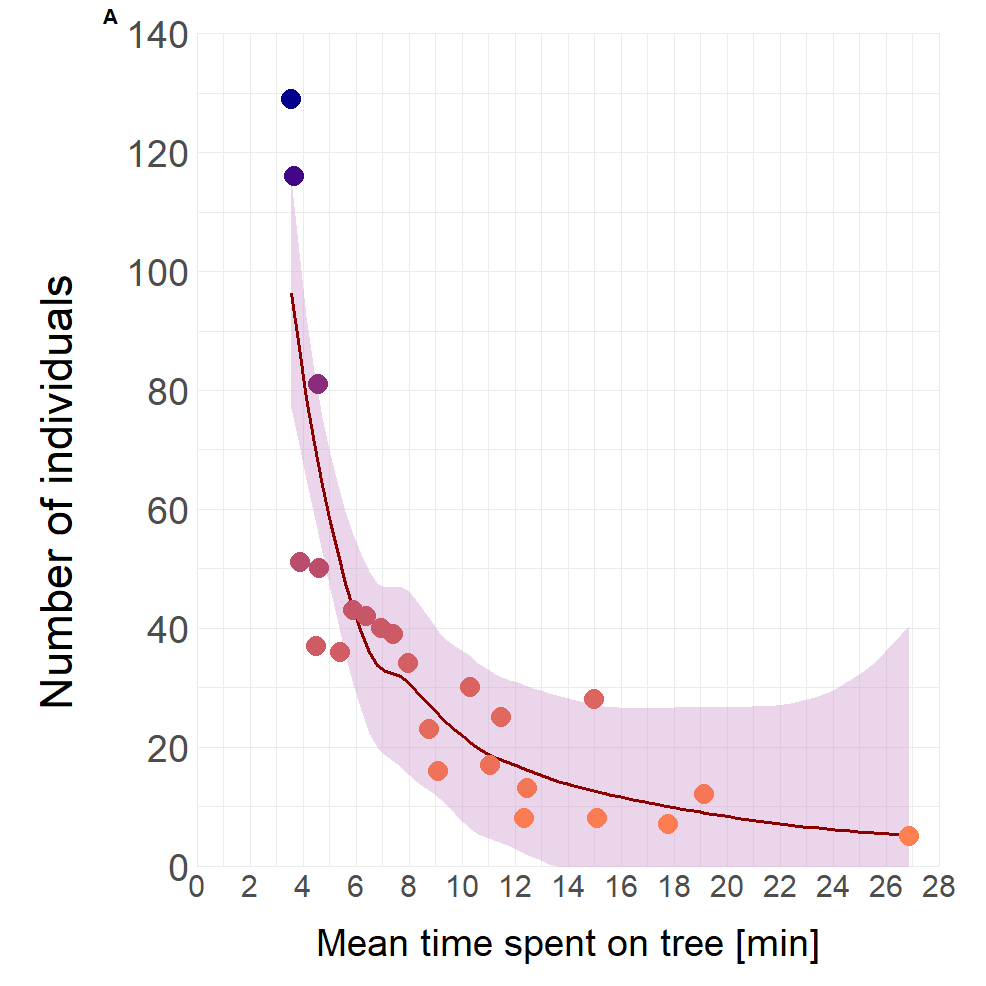
With a higher number of food patches, the activity increased. The activity of bats influences the time spent on the tree. With an increase of individuals per night, the mean time an individual spent on the tree decreases.

Defence Behaviour
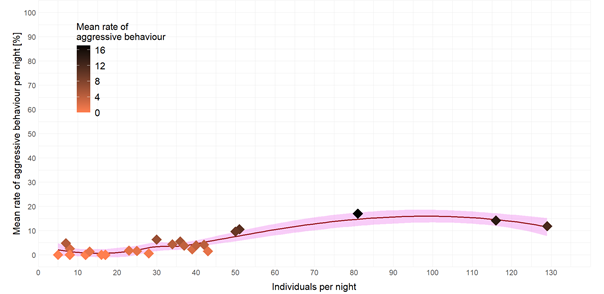
A higher number of individuals during the night increased the rate of aggressive behaviour of the individuals (Figure 4). Subsequently, more individuals on the tree results in a higher likelihood of displaying defence behaviour.
A higher rate of aggression correlated positively with a higher chance of winning the fight (figure 5)