Overview
Along with an increased stand altert, perching and dust bathing behaviour, the enrichment group were found to spend more time in proximity to the novel object than the control group. They also had less amount of fault bars in their feathers than the control group had. The other tests did not show any significant differences.
Details
Ethological study
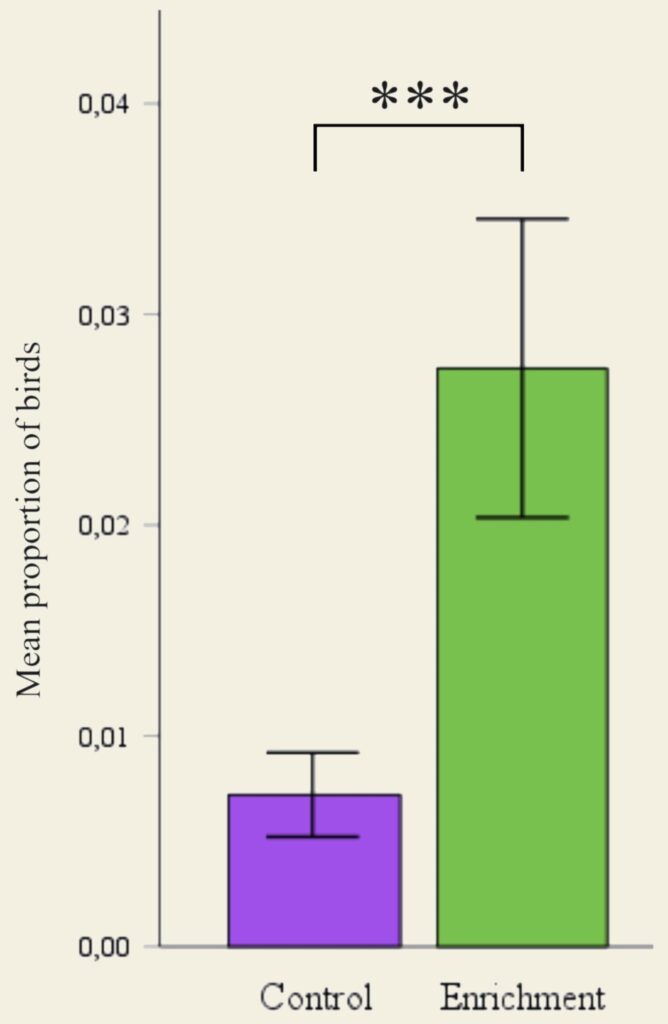
A significant difference between the treatments were found in the following behaviours:
Stand alert
The enrichment group performed the behaviour more than the control group (P=0.040)
Perch
The enrichment group performed the behaviour more than the control group (P=0.008)
Dust bathe
The enrichment group performed the behaviour more than the control group (P=0.001)
No significant differences were found regading the other behaviours.
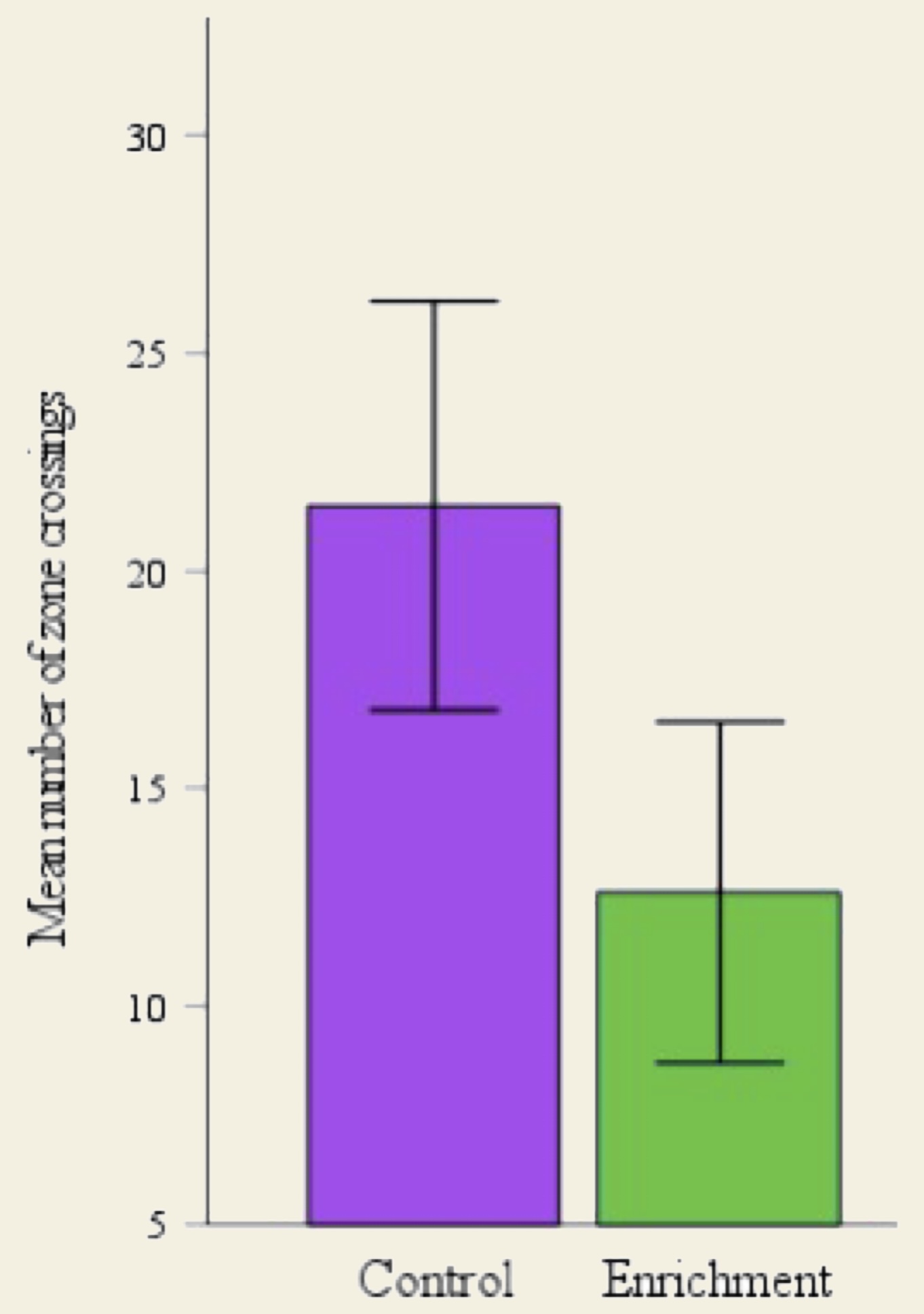
Open field test
There was so significance between the treatments regarding the amount of zone crossings (P=0.138).
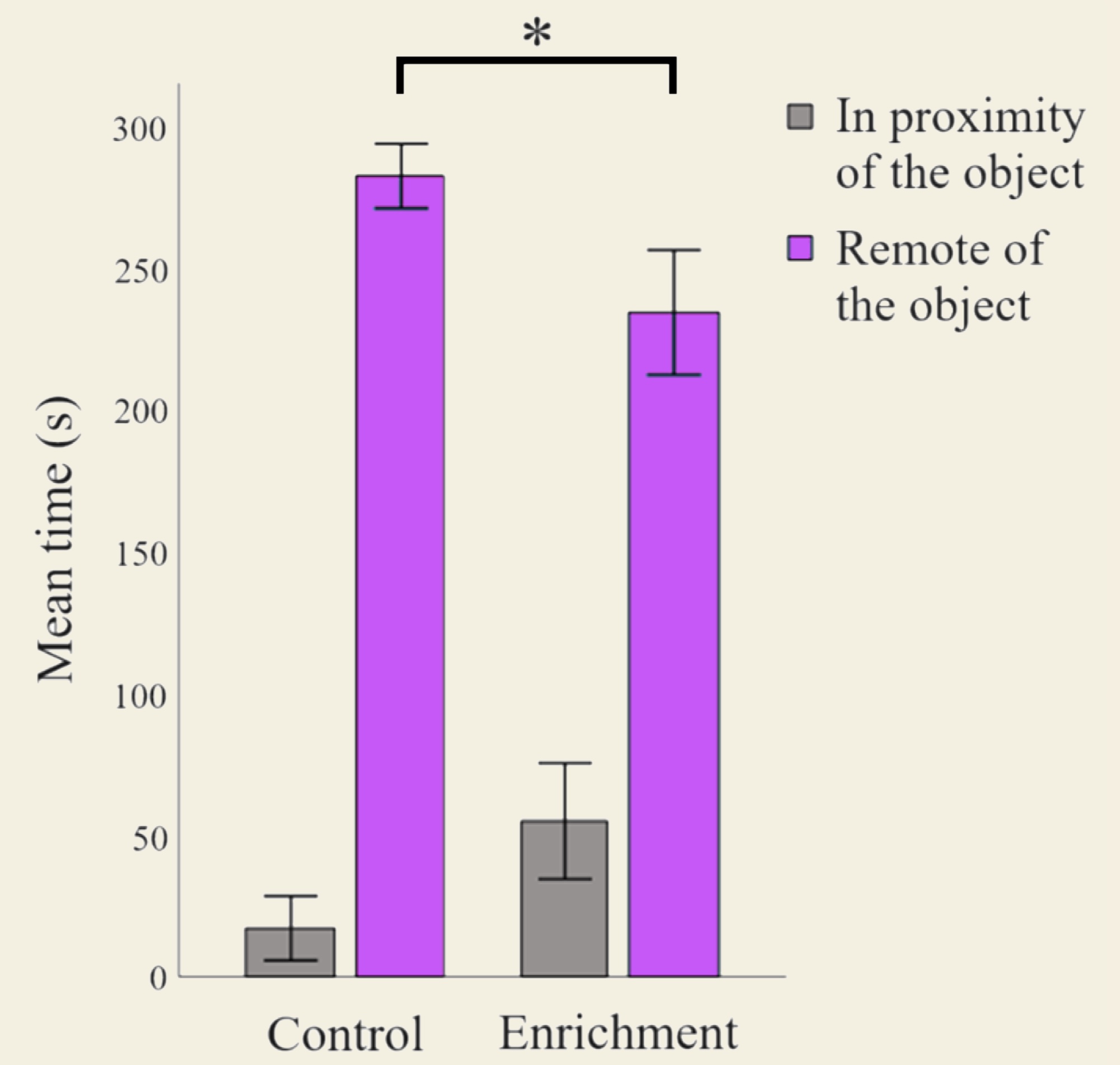
Novel object test
There was a significant difference between the treatments in terms of the amount spent remote of the novel object, where the enrichment group spent less time remote of the object than the control group (P=0.048).
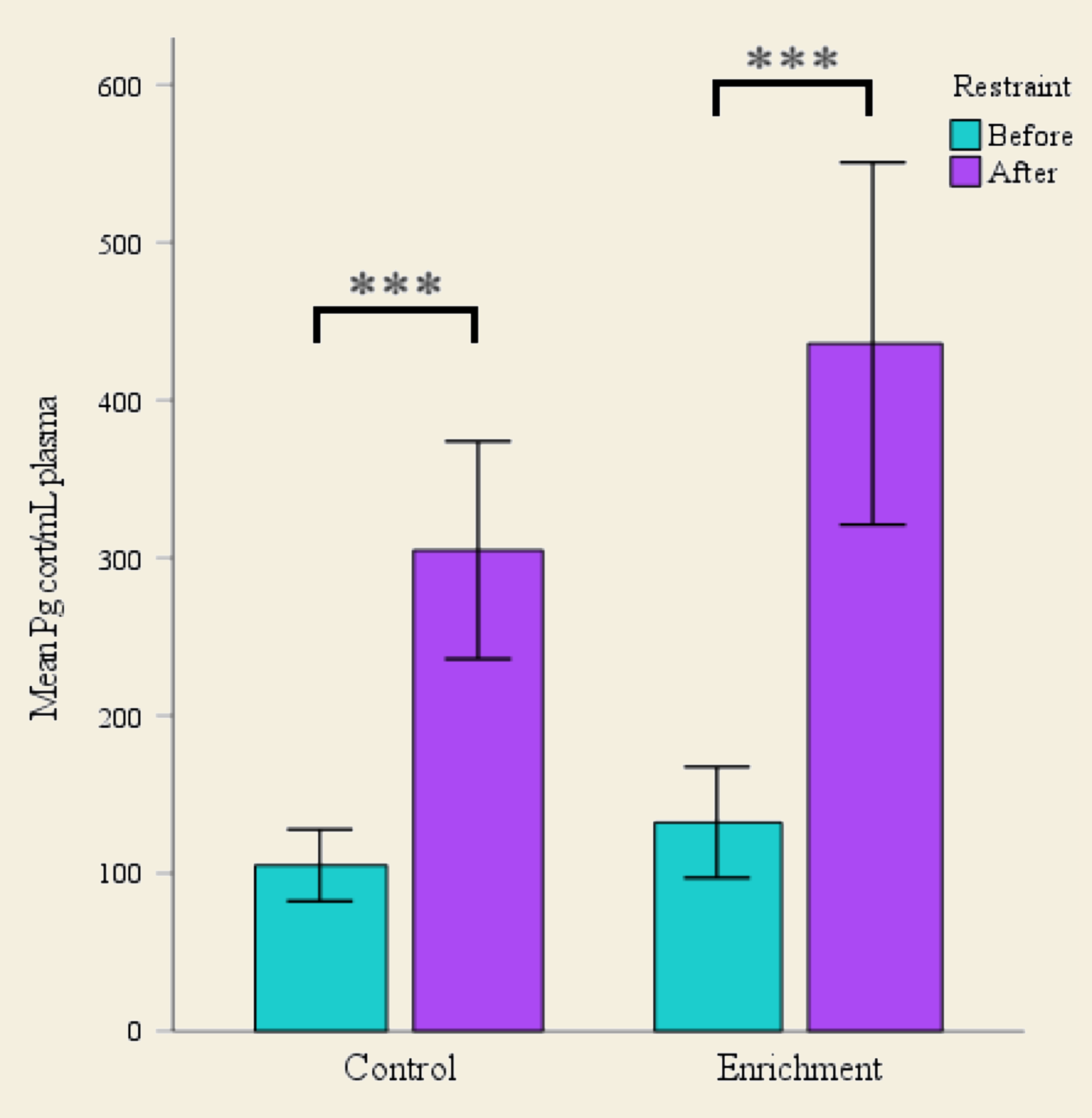
Restraint test
There was no difference between treatments regarding the amount of CORT-levels in the plasma (P=0.587). However, there was a difference between before and after restraint, where the amount increased significantly after the test (P=<0.001).
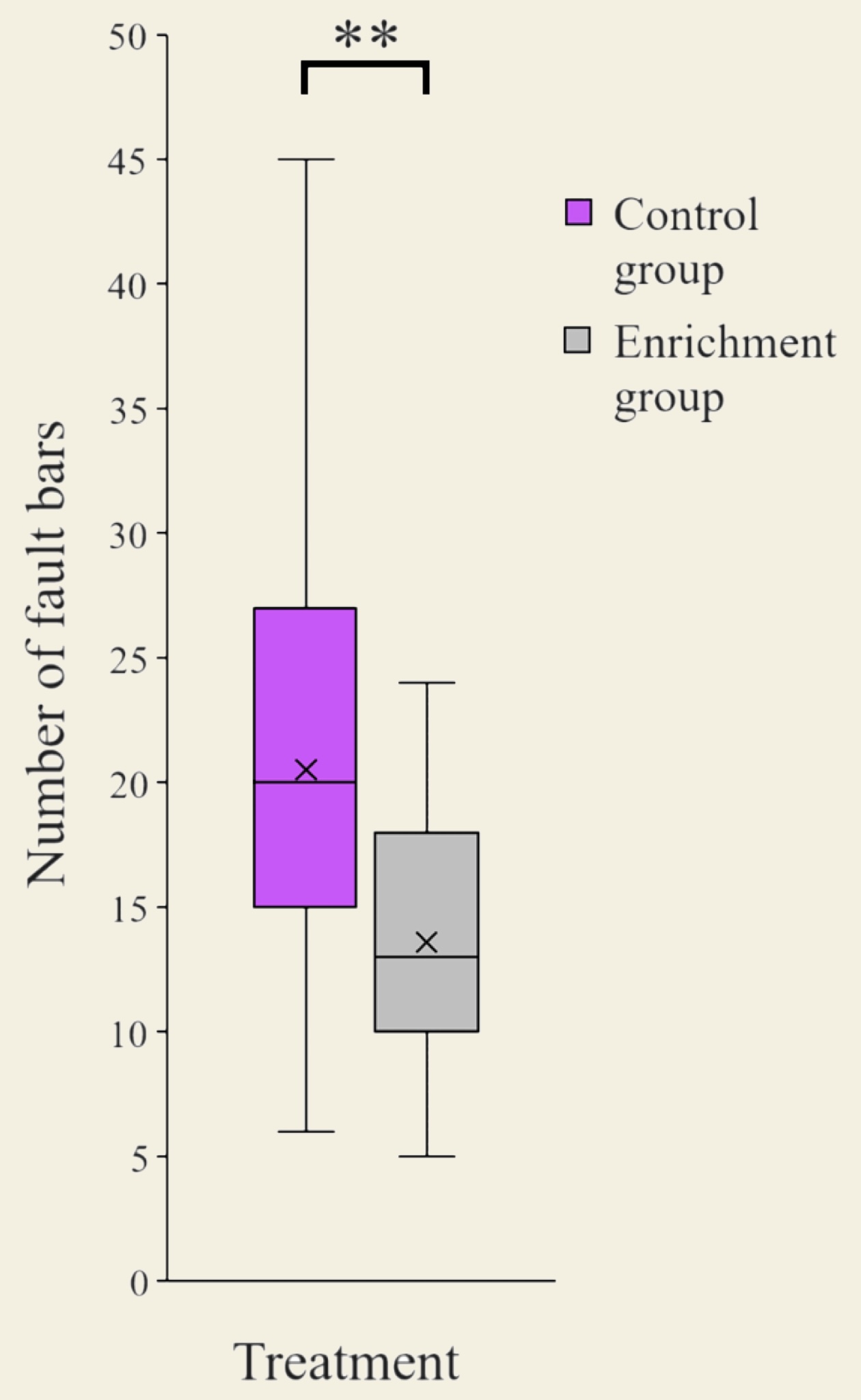
Fault bars analysis
A significant difference was found between the treatments, where the control group had more fault bars than the enrichment group (P=0.003).