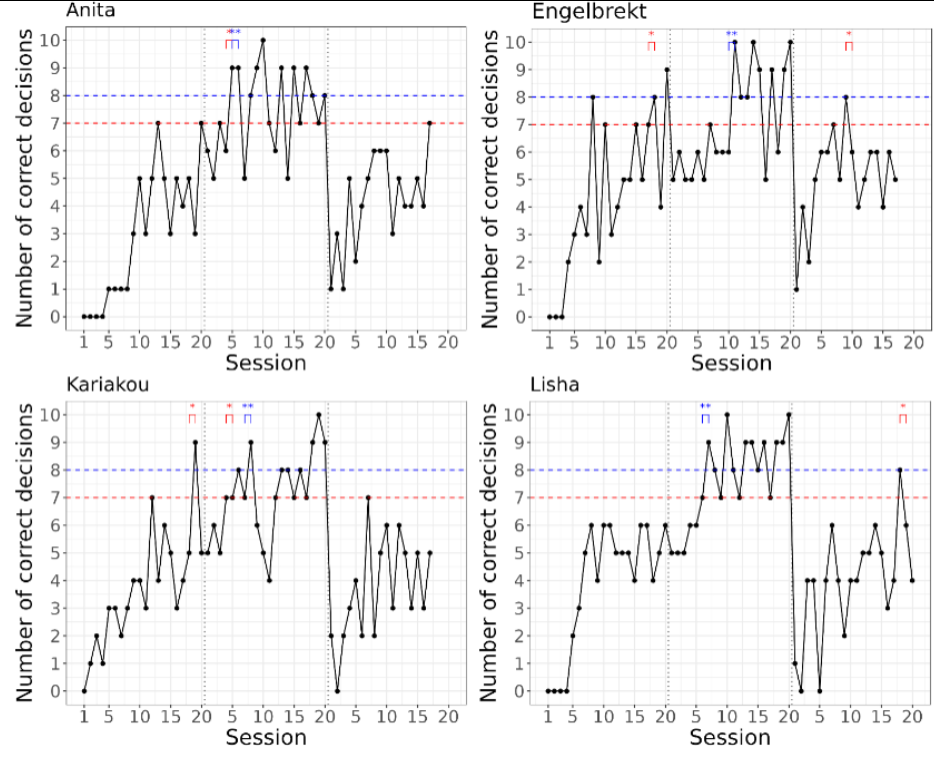
Object permanence test
All animals but one lemur reached the learning criterion of 70% in the object permanence tests, within the 10 sessions. Comparing the performance between species, the sakis needed fewer sessions to reach the 70% and 80% learning criterions compared to the lemurs. The lemurs however, reached the 80% learning criterion with more individuals compared to the sakis.
Lemurs
A majority of the lemurs were successful in the object permanence test, where four out of five lemurs reached the 70% learning criterion at a mean of 4.3 sessions.
The same four out of five lemurs also reached the 80% learning criterion at a mean of 6.8 sessions. Across the sessions, there was a significant increase in mean score (Spearman’s correlation test, rs=0.43, P<0.001).
Sakis
All four sakis were successful in the object permanence test, reaching the 70% learning criterion at a mean of 2.8 sessions.
Three out of four sakis also reached the 80% learning criterion at a mean of 4.3 sessions. In this species, however, there was no increase in mean score across sessions. (Spearman’s correlation test, rs=0.10, P>0.05).
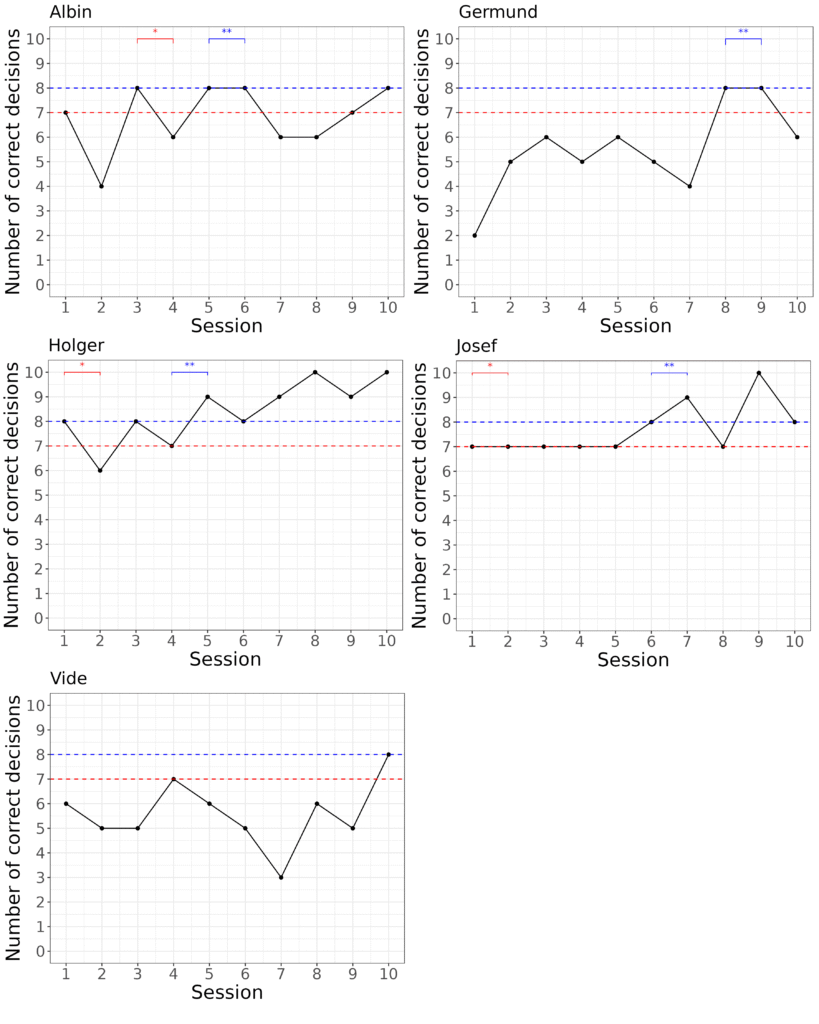
Visual associative learning test
All animals but one lemur reached the learning criterion of 70% in the visual associative learning test, within the 20 sessions. Comparing the performance between species, the lemurs and sakis reached both criterions at approximately the same mean number of sessions, with lemurs taking slightly longer to reach the 70% learning criterion, but slightly faster to reach the 80% learning criterion.
Lemurs
A majority of the lemurs were successful in the object permanence test, where four out of five lemurs reached the 70% learning criterion at a mean of 4.3 sessions.
The same four out of five lemurs also reached the 80% learning criterion at a mean of 6.8 sessions. Across the sessions, there was a significant increase in mean score (Spearman’s correlation test, rs=0.43, P<0.001).

Sakis
All four sakis were successful in the object permanence test, reaching the 70% learning criterion at a mean of 2.8 sessions.
Three out of four sakis also reached the 80% learning criterion at a mean of 4.3 sessions. In this species, however, there was no increase in mean score across sessions. (Spearman’s correlation test, rs=0.10, P>0.05).

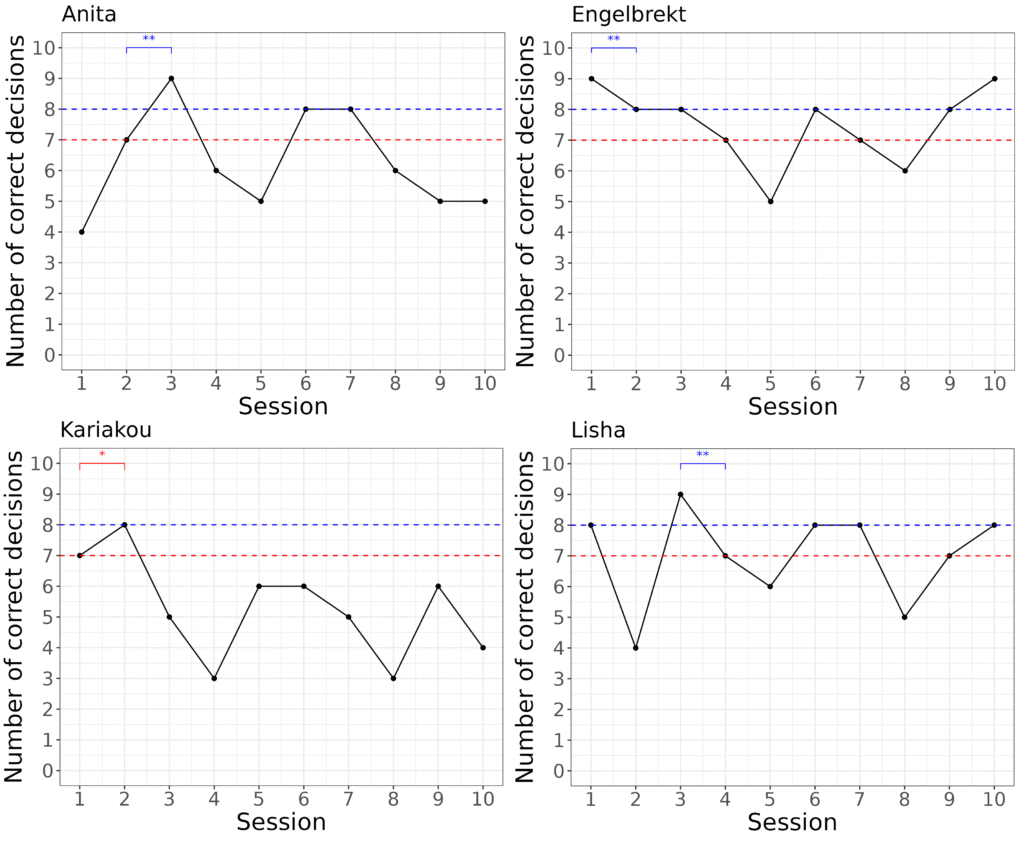
Visual stimulus reversal learning test
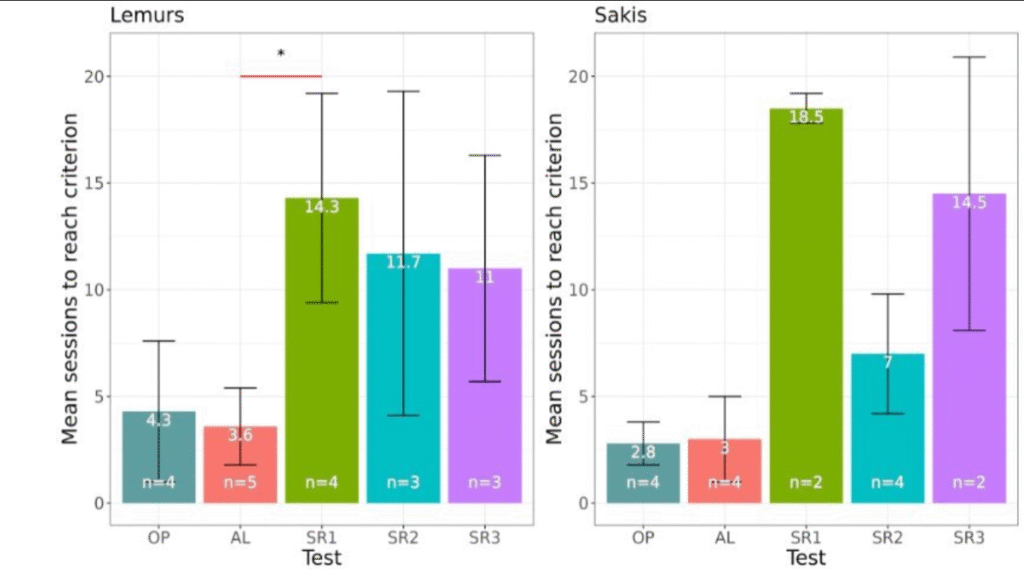
Three reversals (SR1, SR2 & SR3) was performed in the visual stimulus reversal learning test. Comparing scores between the two species, the lemurs and sakis reached the 70% learning criterion in the visual associative learning test after a mean of 3.6 sessions for the lemurs, and 3.0 sessions for the sakis. Both species then displayed a marked increase in sessions required to reach the learning criterion in reversal 1. Compared to the lemurs, however, fewer sakis reached the learning criterion, and they required more sessions to do so. In reversal 2, the mean number of sessions required then decreased for both species, with the sakis requiring a lower mean number of sessions to reach the learning criterion compared to the lemurs. Further, more sakis than lemurs succeeded in reversal 2. In reversal 3, the mean number of sessions required to reach the learning criterion slightly decreased for the lemurs, while it increased markedly in the sakis. Here, a higher number of lemurs reached the learning criterion compared to the sakis.
Lemurs
For SR1, 4/4 lemurs reached the 70% criterion at a mean of 14.25 sessions.
For SR2, 3/4 lemurs reached the 70% criterion at a mean of 11.7 sessions.
For SR3, 3/4 lemurs reached the 70% criterion at a mean of 11 sessions.
For all three reversals, the lemurs showed a Significant increase in mean score.
(Spearman’s correlation test, rs(SR1)=0.71, rs(SR2)=0.49, rs(SR3)=0.71, p<0.01).
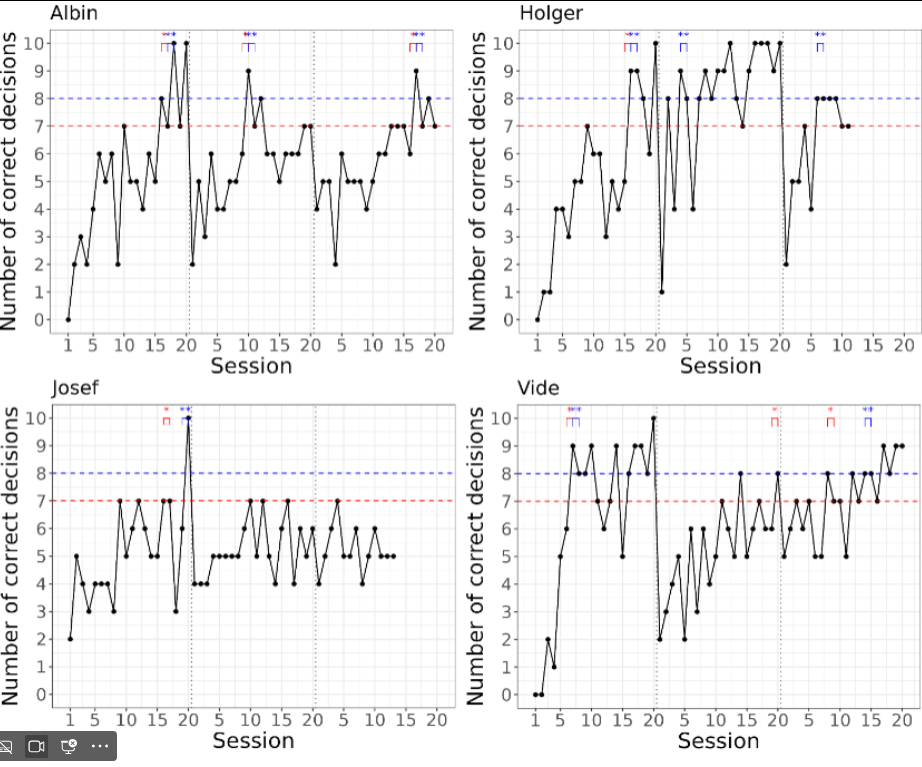
Sakis
For SR1, 2/4 sakis reached the 70% criterion at a mean of 18.5 sessions.
For SR2, 4/4 sakis reached the 70% criterion at a mean of 7 sessions.
For SR3, 2/4 sakis reached the 70% criterion at a mean of 14 sessions.
For all three reversals, the sakis showed a Significant increase in mean score.
(Spearman’s correlation test, rs(SR3)=0.75, rs(SR2)=76, rs(SR3)=44 p<0.01).