Subjects
Black garden ants – Lasius niger
5 colonies were tested between May and December 2024
The ants tested in this study were foragers. Foragers were selected because this caste includes ants that leave the nest in search of food under natural conditions, therefore, this caste is most likely to develop a stimulus-food reward association.

Stimuli
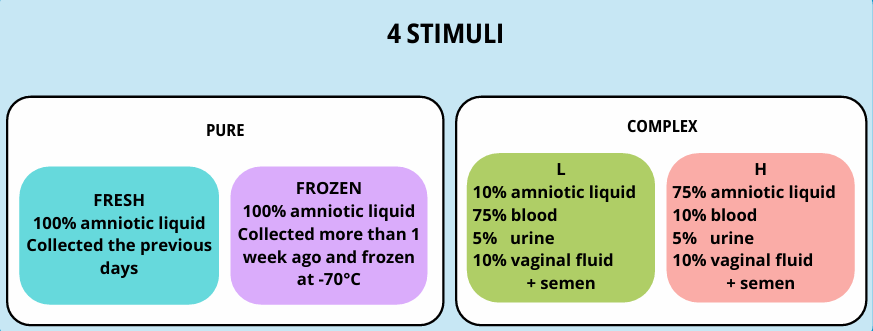
In a clinical setting, premature rupture of amniotic membranes is diagnosed by analysing the vaginal discharge, which is composed of multiple biological fluids. Thus, two of the stimuli tested, referred to as “complex”, were a mixture of amniotic fluid, blood, vaginal liquid, and urine collected from female volunteers at term.
Amniotic fluid was collected via aspiration during caesarean births at the university hospital. Blood, urine and vaginal liquid was also collected from the same anonymous volunteers.
Some of the complex stimuli also contained 10µL of semen to account for the possibility of the women needing a diagnosis having had sex in the days preceding sampling of a vaginal swab.
Training
The pure stimuli were tested against milliQ water and the complex stimuli were tested against a blank similar in composition but without amniotic fluid.
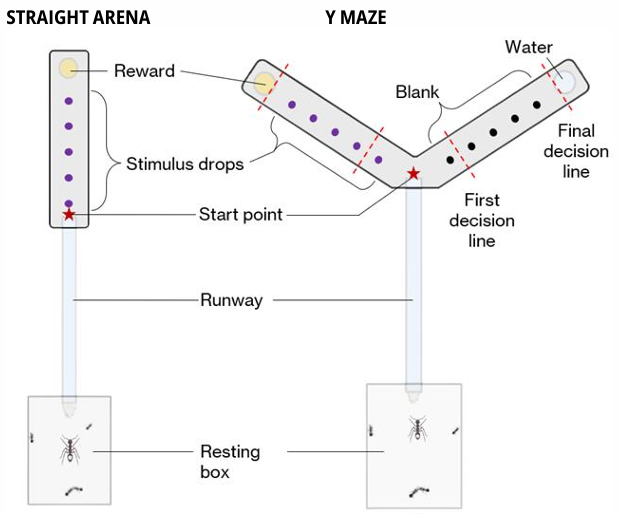
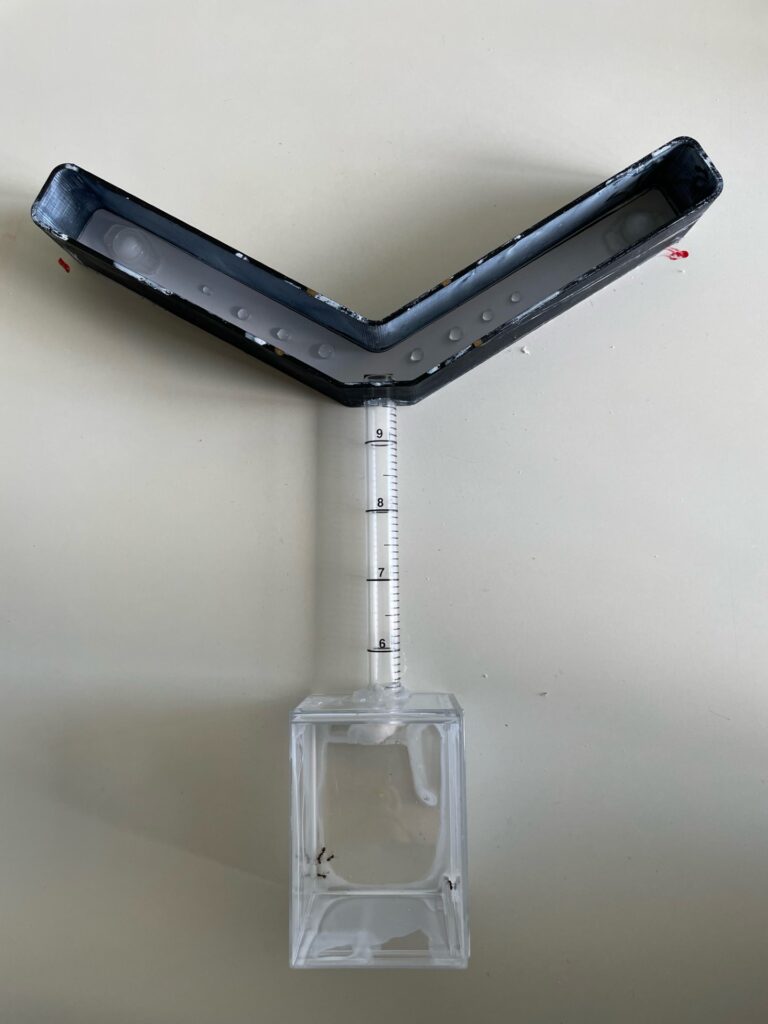
I used two training paradigms – straight arena & Y maze – to understand if one would provide better results than the other during the testing phase.
- 6 trials
- 5 minutes each
- 5 minutes of rest in between
- Honey-water reward
Testing
- Same set-up as the training but only in the Y maze
- No reward
- 2 trials
- 5 minute
- 5 minute rest in between

What I measured
- Straight arena
- Time spent in the runway during the trial
- Latency to reach the rewarded cup
- Y maze
- Time spent in the runway during the trial
- Latency to reach the rewarded cup
- First choice
- Final choice
- Time spent in the rewarded arm