Premature Rupture of Amniotic Membranes
What is it?
- Breakage of the amniotic membranes before the onset of labour.
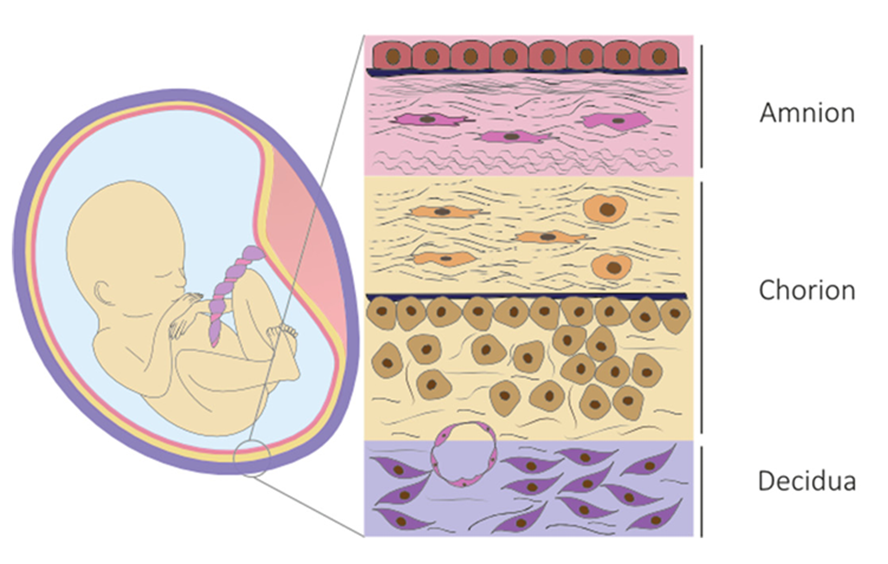
- Foetal membranes consist of the amnion lining the amniotic cavity, and the chorion attached to the maternal decidua. These membranes encapsules the amniotic liquid, which provides a physical barrier to ascending infections.
- Affects approximately 8% of all deliveries.
- Can lead to complications such as infections, respiratory distress and umbilical cord compression.
- Leads to preterm delivery often via labour induction.
Current diagnostic tools
- Ferning pattern test – Air dried vaginal discharge samples form patterns that differ whether amniotic fluid is present ir not.
- pH test – Amniotic fluid has a higher pH than vaginal discharge, samples can be tested with nitrazine paper which will turn blue if amniotic fluid is present.
- Amnioinfusion of indigo carmine – Ultrasound-guided injection of blue dye in the amniotic sac, if the amniotic membranes are broken, vaginal leakage will be blue.
Both ferning pattern and pH test can have inaccurate results due to the presence of other fluids in the discharge. These methods are also limited by the small amount of sample collected which means repeating the tests difficult.
Amnioinfusion is more reliable but is expensive and can lead to complications on its own, like infections or placental abruption.
Currently, there is no reliable, non-invasive, time- and cost-effective diagnostic tool for premature rupture of amniotic membranes.
Animals as diagnostic tools
- Dogs have identified ovarian carcinoma in blood and tissue samples and detected breast cancer in breath samples.
- African giant pouch rats, Cricetomys gambianus, can detect tuberculosis.
Although dogs are well suited for medical diagnosis, training them can take hundreds of trials over several months.
Why ants?
Ants have a well-developed sense of smell, they are quick learners and easy to train. They also have easy accessibility and easy husbandry.
- Why Lasius niger?
- This species is very common in Switzerland
- It had previously learned a stimulus-reward association with a choice accuracy of 71%
Aim
Assess the ability of Lasius niger ants to form a stimulus-reward association between samples containing amniotic liquid and honey-water