The Animals
Dogs
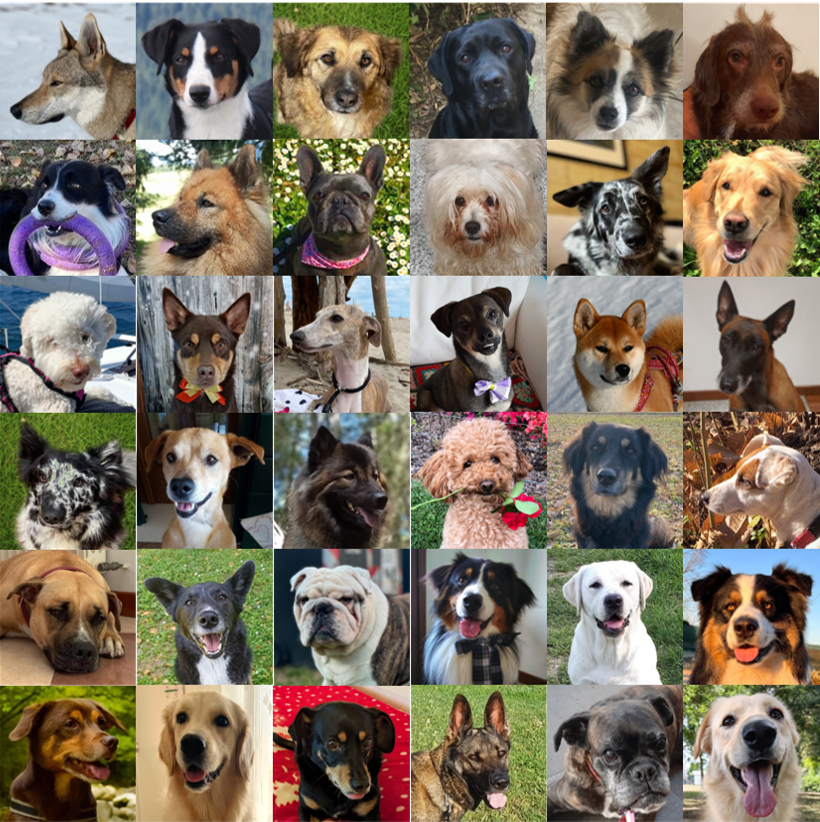

36 privately owned dogs
- Species: Canis familiaris
- Breed: various
- Age: 1-11 years old
- Sex: 13 males, 23 females
Wolves
Pack of 8 captive wolves
- Species: Canis lupus
- Age: 9-12 years old
- Sex: 5 males, 3 females

The Experiment
Setup
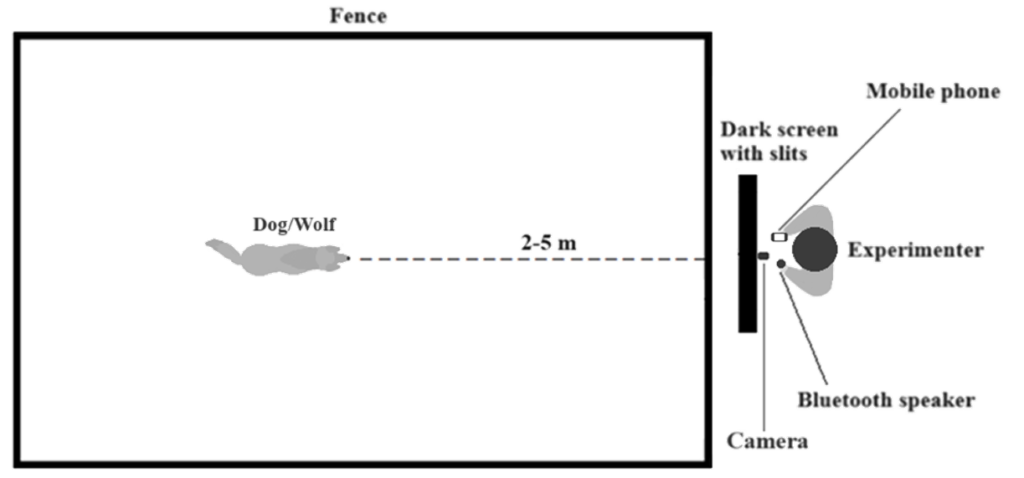
A dark screen with slices in the middle was positioned in front of a fenced area.
The experimenter was positioned behind the dark screen with a mobile phone, a yellow-taped Bluetooth speaker and a camera to record the experiment through one of the slits in the dark screen
The dog-owner dyad or the wolf were inside the fenced area at a 2 to 5 m distance from the dark screen

Procedure
The sound of a squeaky toy was played from different positions using the yellow-taped Bluetooth speaker.
- superior (S) to the subject’s head;
- frontally (F) to the subject’s head;
- laterally (L) to the subject’s head (either left or right).

The sound was played twice in each position:
- once the speaker was visible (V);
- once it was hidden (I).
All the experiment were recorded for later analysis. Take a look!
Analysis
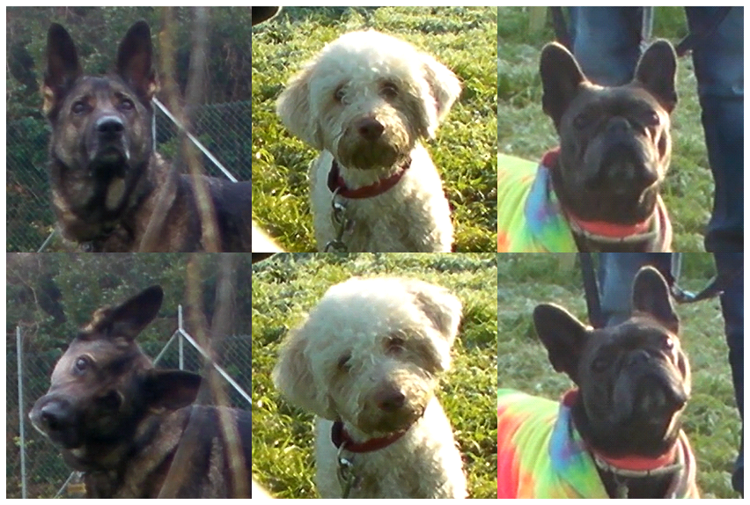

The head tilting behaviour can be defined as a bending movement of the head toward one side.
The head tilting outcome (1 if present, 0 if not) was recorded and the correlation with other variables was analysed (sound source position and visibility, sex, age and breed group of the dogs, their pinnae (ears) shape and muzzle lenght). The data were analysed through generalized linear mixed models (GLMM) (Bolker, 2015), Tukey’s range test and QQ plots using the statistical software R.
Furthermore, the attentiveness (i.e. attention towards the sound origin) of dogs was analyzed through the software for behavioural analysis BORIS (Friard & Gamba, 2016) and the statistical software R (R Core Team, 2021) and RStudio (Posit team, 2023).
Finally, descriptive statistic was used to obtain the owners reported frequency of the head tilting behaviour (answers from owners who were contacted to participate in the experiment but were not able to were included too).
Are you curious about the results?
References
Bolker, B. M. (2015). Linear and generalized linear mixed models. Ecological statistics: contemporary theory and application, 309-333.
Friard, O. & Gamba, M. (2016), BORIS: a free, versatile open-source event-logging software for video/audio coding and live observations. Methods in Ecology and Evolution, 7, 1325–1330. doi:10.1111/2041-210X.12584
Posit team (2023). RStudio: Integrated Development Environment for R [Computer software]. Posit Software. URL http://www.posit.co/
R Core Team (2023). R: A language and environment for statistical computing (R version 4.3.2) [Computer software]. R Foundation for Statistical Computing. https://www.R-project.org/